#4 Top 5 Positive Sustainability News & Insights - Biweekly
Stay updated with the top 5 positive sustainability news highlights from the last two weeks, accompanied by my insights.
#4 Green Swan Pursuit
1. Google Partners with Kairos Power to Deploy Carbon-Free Small Modular Reactors
Brief
In a bold step toward decarbonizing its operations, Google has partnered with nuclear technology company Kairos Power to deploy a fleet of small modular reactors (SMRs) across the US, aiming to generate up to 500 MW of carbon-free energy. This initiative, part of Google’s goal to operate on 24/7 carbon-free energy by 2030, comes as the tech giant grapples with the soaring energy demands of its AI-driven data centers.
Why It Matters
The global data center industry is projected to emit 2.5 billion tons of CO2 by 2030—about 40% of the U.S.'s annual emissions, according to Morgan Stanley. Google’s greenhouse gas emissions have surged by 48% over the past five years, driven largely by energy-hungry data centers. In 2023 alone, Google’s emissions rose by 13%, reaching 14.3 million tonnes.
Nuclear’s Strategic Role:
Nuclear power is poised to play a critical role in addressing these rising energy demands. On a life-cycle basis, nuclear power emits only 12g of CO2 equivalent per kWh—comparable to wind and significantly lower than solar, making it one of the most carbon-efficient energy sources available.
Tech Industry Leaders Back Nuclear: Google’s move mirrors similar actions by other tech giants, such as Microsoft, which has entered into a 20-year power purchase agreement to restart the Three Mile Island Unit 1 nuclear reactor to power its data centers. Prominent figures like Bill Gates and Sam Altman are also at the forefront of nuclear energy advocacy, with startups like TerraPower and Oklo pushing the boundaries of nuclear innovation.
Small Reactors, Big Solutions: Small modular reactors from innovators like Kairos Power and Last Energy offer scalable, reliable, carbon-free energy. With a smaller footprint and faster deployment, they're ideal for powering energy-intensive operations like data centers.

Insights
Google’s decision to embrace nuclear technology reflects a strategic shift towards securing stable, reliable, carbon-free energy amid the exploding demand from AI-driven data centers. While renewable sources like wind and solar are crucial, they face challenges of intermittency and storage. SMRs offer a stable, 24/7 energy supply, making them an ideal complement. With AI projected to consume 4.5% of global energy by 2030, the tech sector cannot rely solely on renewables without exacerbating the climate crisis.
2. Scientists Successfully Breed Corals to Improve Their Heat Tolerance
Brief
In a groundbreaking study, scientists at Newcastle University's Coralassist Lab have successfully conducted selective breeding trials aimed at enhancing coral heat tolerance. The trials involved two distinct types of heat exposure:
Short, intense heat exposure (10 days, +3.5°C)
Long-term, less intense exposure (1 month, +2.5°C)
The results are promising: offspring from parent colonies selected for higher heat resilience demonstrated increased tolerance to both types of exposure. Theoretically, this breeding method could improve coral heat tolerance by roughly 1°C per week within a single generation.
Why It Matters
The global coral bleaching crisis has reached unprecedented levels, with bleaching recorded in 62 countries from February 2023 to April 2024. The Great Barrier Reef has been particularly hard-hit, with nearly 80% of its coral outcrops affected1. This global crisis underscores the critical need for solutions like selective breeding, as coral reefs are integral to both marine ecosystems and the global economy.
Ecological Importance: Coral reefs support 25% of marine life, making them foundational to ocean biodiversity. Their decline could result in significant ecosystem shifts, including the loss of key fish species that rely on the reefs for shelter and food.
Economic Value: Coral reefs contribute an estimated $375 billion annually in goods and services2. This includes:
$9.6 billion from tourism and recreation
$9.0 billion from coastal protection
$5.7 billion from fisheries
$5.5 billion from biodiversity
Insights
This research not only marks a critical step in coral conservation but also highlights the alarming sensitivity of these ecosystems. A mere 1°C increase in water temperature over four weeks can trigger mass bleaching events. Coral bleaching occurs when corals expel their symbiotic algae (zooxanthellae) due to stress, causing them to turn white. While bleaching does not necessarily mean the coral is dead, it significantly impacts the coral’s health and its ability to recover.
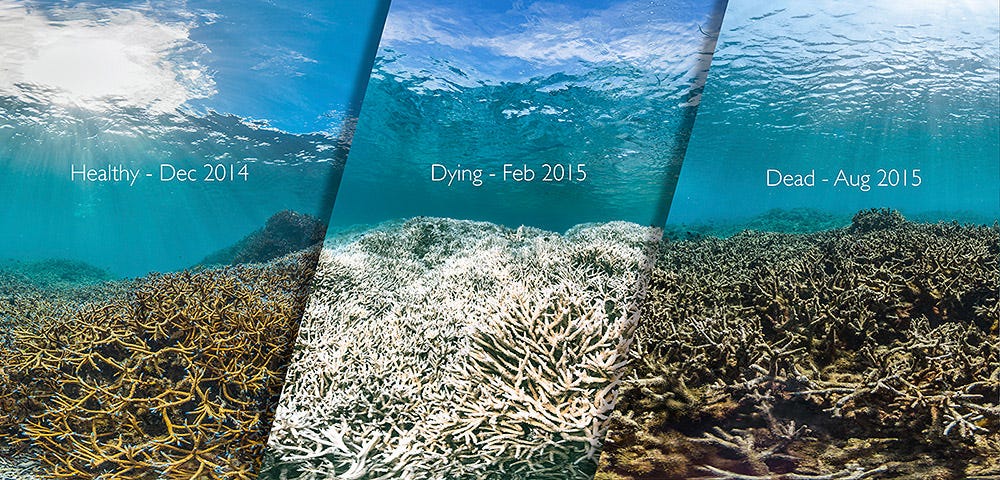

Potential for Recovery: Corals can recover from bleaching if favorable conditions return within 3-6 months, though the recovery process is slow. Full reef recovery may take up to 12 years, assuming no further disturbances.
Long-term Impacts: Even if corals survive bleaching, they may suffer from reduced growth rates, decreased reproductive success, and higher vulnerability to diseases.
3. Renewable Energy Poised to Power Nearly Half of Global Demand by 2030
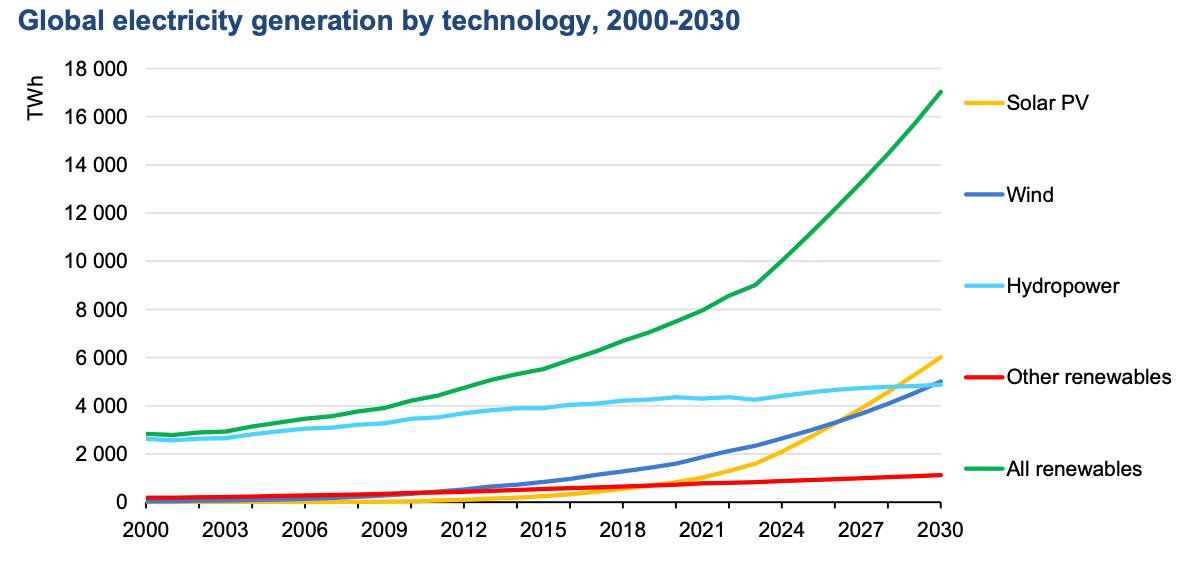
Brief
The International Energy Agency (IEA) has revealed that while renewable energy is on track to meet nearly half of global electricity demand by 2030, it will fall short of the ambitious COP28 goal to triple global renewable capacity by that year. Over 5,500 GW of new renewable capacity—equivalent to the combined power capacity of China, the EU, India, and the US—will be added, but achieving the target requires 25 million kilometers of grid upgrades and 1,500 GW of energy storage. Solar photovoltaic (PV) technology will drive 80% of this growth, but the rapid increase in solar manufacturing has led to oversupply and financial losses for manufacturers. China will account for 60% of global expansion, while 70 countries are on track to meet or exceed their renewable targets.
Why It Matters
This report highlights both the rapid progress in renewable energy and the obstacles that remain. While renewable energy is increasingly the cheapest option worldwide, key infrastructure challenges—particularly in grid expansion and energy storage—are threatening to slow down the pace of the energy transition. The inability to meet the COP28 target could hinder global efforts to reduce emissions and limit climate change, even as renewable technologies continue to advance.
Global Leadership in Renewables: China’s dominance in the renewable sector highlights both the opportunity and challenge of rapid energy transition. While the country’s expansion is crucial, it also underscores the need for more equitable global distribution of renewable capacity growth, particularly in regions like Africa and Southeast Asia, which have vast potential but require investment and infrastructure.
Infrastructure Bottleneck: The sheer scale of grid and storage upgrades required—25 million kilometers of new grid lines and 1,500 GW of energy storage—is a stark reminder that producing renewable energy is only part of the solution. Ensuring that this energy can be efficiently transmitted and stored is equally critical.
Insights
This report illustrates the complex interplay between technological advancement and infrastructure readiness in the global energy transition. Solar PV's dominance in the growth mix points to the maturity and scalability of solar technology, but oversupply and financial stress for manufacturers reveal the volatility of the market.
Without the necessary grid infrastructure and energy storage solutions, the risk is that renewable energy growth could be stunted by operational inefficiencies, despite the availability of cleaner energy sources.
4. The new fashion: Clothes that help combat rising temperatures
Brief
Researchers from Zhengzhou University and the University of South Australia have developed a novel fabric designed to counter rising urban temperatures. This three-layered textile reflects sunlight, allows heat to escape, and lowers temperature. In experiments, the fabric was found to be 2.3°C cooler than traditional textiles and up to 6.2°C cooler than the surrounding environment when used as a horizontal surface covering. The technology aims to provide a sustainable alternative to conventional air conditioning, potentially reducing energy consumption and strain on power grids during heatwaves.
Why It Matters
Urban Heat Mitigation: By 2050, 68% of the global population will live in urban areas, where the urban heat island effect raises temperatures by 1-3°C. Cooling fabrics could reduce heat stress in these regions.
Energy Savings: Air conditioning accounts for around 10% of global electricity consumption. Cooling fabrics, by reducing the need for air conditioning, could help lower energy demand and reduce emissions.
Sustainability in Fashion: The global cooling fabrics market, valued at $1.69 billion in 2023, is projected to grow at a CAGR of 8.3% through 2030, as consumers increasingly seek eco-friendly, climate-conscious solutions.
Insights
Hopefully, this won’t be the only fashion news I get to review on my blog :)
Cooling fabrics act as a small-scale solution for temperature regulation, mirroring the principles of geoengineering, which aims to cool the planet by reflecting sunlight. Techniques like solar radiation management share similarities with these fabrics, both focusing on reflecting heat to manage rising temperatures. While geoengineering tackles climate change on a global scale, cooling fabrics provide an immediate, accessible way for individuals to adapt to rising temperatures in daily life.
5. Toyota Invests $500 Million in Joby Aviation, Boosting Electric Air Taxi

Brief
Electric air taxi startup Joby Aviation has secured a $500 million investment from Toyota, bringing the automaker’s total investment in the company to $894 million. By 2025, Toyota will own over 20% of Joby, reinforcing its commitment to the electric vertical takeoff and landing (eVTOL) market. Joby aims to produce one eVTOL per month by the end of 2024, with plans to launch a public air taxi service accessible via apps like Uber.
Why It Matters
This partnership highlights the push to decarbonize urban transportation. Fossil fuel-powered taxis emit around 4.6 metric tons of CO2 annually, contributing to urban pollution. In contrast, electric air taxis promise zero-emission flights, offering a cleaner solution for short, high-traffic city routes.
Insights
The eVTOL market is expected to reach over $1 trillion by 2040, according to Morgan Stanley. Toyota’s investment in Joby signals a strategic shift toward air mobility as a key player in sustainable transportation. Replacing a portion of the 100 million ride-sharing vehicles on the road today with electric air taxis could drastically reduce urban emissions.
Thanks :)
Wanna read more?
Enjoying my writing? Wanna join me on the road and support my work?
Stay tuned for the next blog post coming in two weeks!
Until then, take care!
www.unep.org
reefresilience.org







